assess performance of a 'glmnet' object using test data.
assess.glmnet.RdGiven a test set, produce summary performance measures for the glmnet model(s)
Arguments
- object
Fitted
"glmnet"or"cv.glmnet","relaxed"or"cv.relaxed"object, OR a matrix of predictions (forroc.glmnetorassess.glmnet). Forroc.glmnetthe model must be a 'binomial', and forconfusion.glmnetmust be either 'binomial' or 'multinomial'- newx
If predictions are to made, these are the 'x' values. Required for
confusion.glmnet- newy
required argument for all functions; the new response values
- weights
For observation weights for the test observations
- family
The family of the model, in case predictions are passed in as 'object'
- ...
additional arguments to
predict.glmnetwhen "object" is a "glmnet" fit, and predictions must be made to produce the statistics.
Value
assess.glmnet produces a list of vectors of measures.
roc.glmnet a list of 'roc' two-column matrices, and
confusion.glmnet a list of tables. If a single prediction is
provided, or predictions are made from a CV object, the latter two drop the
list status and produce a single matrix or table.
Details
assess.glmnet produces all the different performance measures
provided by cv.glmnet for each of the families. A single vector, or a
matrix of predictions can be provided, or fitted model objects or CV
objects. In the case when the predictions are still to be made, the
... arguments allow, for example, 'offsets' and other prediction
parameters such as values for 'gamma' for 'relaxed' fits. roc.glmnet
produces for a single vector a two column matrix with columns TPR and FPR
(true positive rate and false positive rate). This object can be plotted to
produce an ROC curve. If more than one predictions are called for, then a
list of such matrices is produced. confusion.glmnet produces a
confusion matrix tabulating the classification results. Again, a single
table or a list, with a print method.
See also
cv.glmnet, glmnet.measures and vignette("relax",package="glmnet")
Examples
data(QuickStartExample)
x <- QuickStartExample$x; y <- QuickStartExample$y
set.seed(11)
train = sample(seq(length(y)),70,replace=FALSE)
fit1 = glmnet(x[train,], y[train])
assess.glmnet(fit1, newx = x[-train,], newy = y[-train])
#> $mse
#> s0 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6
#> 10.5356884 10.0473027 9.5757375 8.7448060 8.0414304 7.4451552 6.8302096
#> s7 s8 s9 s10 s11 s12 s13
#> 6.2099274 5.5979797 4.8918587 4.2620453 3.7367187 3.2983155 2.9322791
#> s14 s15 s16 s17 s18 s19 s20
#> 2.6265064 2.3709330 2.1242795 1.9219451 1.7587268 1.6226452 1.5091624
#> s21 s22 s23 s24 s25 s26 s27
#> 1.4144863 1.3354649 1.2694776 1.2143453 1.1682560 1.1297026 1.0974313
#> s28 s29 s30 s31 s32 s33 s34
#> 1.0652936 1.0249928 0.9930414 0.9659219 0.9435578 0.9249772 0.9096485
#> s35 s36 s37 s38 s39 s40 s41
#> 0.8970118 0.8866020 0.8773197 0.8703946 0.8648273 0.8609494 0.8597018
#> s42 s43 s44 s45 s46 s47 s48
#> 0.8588511 0.8629691 0.8674411 0.8722799 0.8776263 0.8827885 0.8870380
#> s49 s50 s51 s52 s53 s54 s55
#> 0.8911607 0.8951440 0.8989787 0.9030727 0.9070581 0.9109051 0.9145902
#> s56 s57 s58 s59 s60 s61 s62
#> 0.9180974 0.9211897 0.9242868 0.9272307 0.9299921 0.9325693 0.9349674
#> s63 s64 s65 s66 s67 s68
#> 0.9371937 0.9392563 0.9411642 0.9426805 0.9445011 0.9458195
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean-Squared Error"
#>
#> $mae
#> s0 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6 s7
#> 2.6946299 2.6328780 2.5673994 2.4405206 2.3249133 2.2195763 2.1151049 2.0115127
#> s8 s9 s10 s11 s12 s13 s14 s15
#> 1.9030069 1.7718821 1.6518698 1.5453805 1.4483515 1.3599423 1.2793871 1.2066589
#> s16 s17 s18 s19 s20 s21 s22 s23
#> 1.1339882 1.0695296 1.0150683 0.9781225 0.9498621 0.9241123 0.9006501 0.8811996
#> s24 s25 s26 s27 s28 s29 s30 s31
#> 0.8651666 0.8551227 0.8495833 0.8445360 0.8380969 0.8279767 0.8194392 0.8094367
#> s32 s33 s34 s35 s36 s37 s38 s39
#> 0.7996659 0.7907266 0.7838971 0.7794754 0.7754465 0.7704058 0.7660117 0.7621631
#> s40 s41 s42 s43 s44 s45 s46 s47
#> 0.7588402 0.7581804 0.7579210 0.7600092 0.7619297 0.7637101 0.7657734 0.7688329
#> s48 s49 s50 s51 s52 s53 s54 s55
#> 0.7717302 0.7744494 0.7769264 0.7797273 0.7827940 0.7855762 0.7881095 0.7904177
#> s56 s57 s58 s59 s60 s61 s62 s63
#> 0.7925209 0.7943038 0.7960365 0.7976354 0.7990963 0.8004283 0.8016421 0.8027481
#> s64 s65 s66 s67 s68
#> 0.8037558 0.8046740 0.8053809 0.8062495 0.8068503
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean Absolute Error"
#>
preds = predict(fit1, newx = x[-train, ], s = c(1, 0.25))
assess.glmnet(preds, newy = y[-train], family = "gaussian")
#> $mse
#> s1 s2
#> 7.312414 1.498532
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean-Squared Error"
#>
#> $mae
#> s1 s2
#> 2.1976089 0.9470799
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean Absolute Error"
#>
fit1c = cv.glmnet(x, y, keep = TRUE)
fit1a = assess.glmnet(fit1c$fit.preval, newy=y,family="gaussian")
plot(fit1c$lambda, log="x",fit1a$mae,xlab="Log Lambda",ylab="Mean Absolute Error")
abline(v=fit1c$lambda.min, lty=2, col="red")
 data(BinomialExample)
x <- BinomialExample$x; y <- BinomialExample$y
fit2 = glmnet(x[train,], y[train], family = "binomial")
assess.glmnet(fit2,newx = x[-train,], newy=y[-train], s=0.1)
#> $deviance
#> s1
#> 1.037535
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Binomial Deviance"
#>
#> $class
#> s1
#> 0.1333333
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Misclassification Error"
#>
#> $auc
#> [1] 0.9351852
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "AUC"
#>
#> $mse
#> s1
#> 0.333371
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean-Squared Error"
#>
#> $mae
#> s1
#> 0.7909957
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean Absolute Error"
#>
plot(roc.glmnet(fit2, newx = x[-train,], newy=y[-train])[[10]])
data(BinomialExample)
x <- BinomialExample$x; y <- BinomialExample$y
fit2 = glmnet(x[train,], y[train], family = "binomial")
assess.glmnet(fit2,newx = x[-train,], newy=y[-train], s=0.1)
#> $deviance
#> s1
#> 1.037535
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Binomial Deviance"
#>
#> $class
#> s1
#> 0.1333333
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Misclassification Error"
#>
#> $auc
#> [1] 0.9351852
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "AUC"
#>
#> $mse
#> s1
#> 0.333371
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean-Squared Error"
#>
#> $mae
#> s1
#> 0.7909957
#> attr(,"measure")
#> [1] "Mean Absolute Error"
#>
plot(roc.glmnet(fit2, newx = x[-train,], newy=y[-train])[[10]])
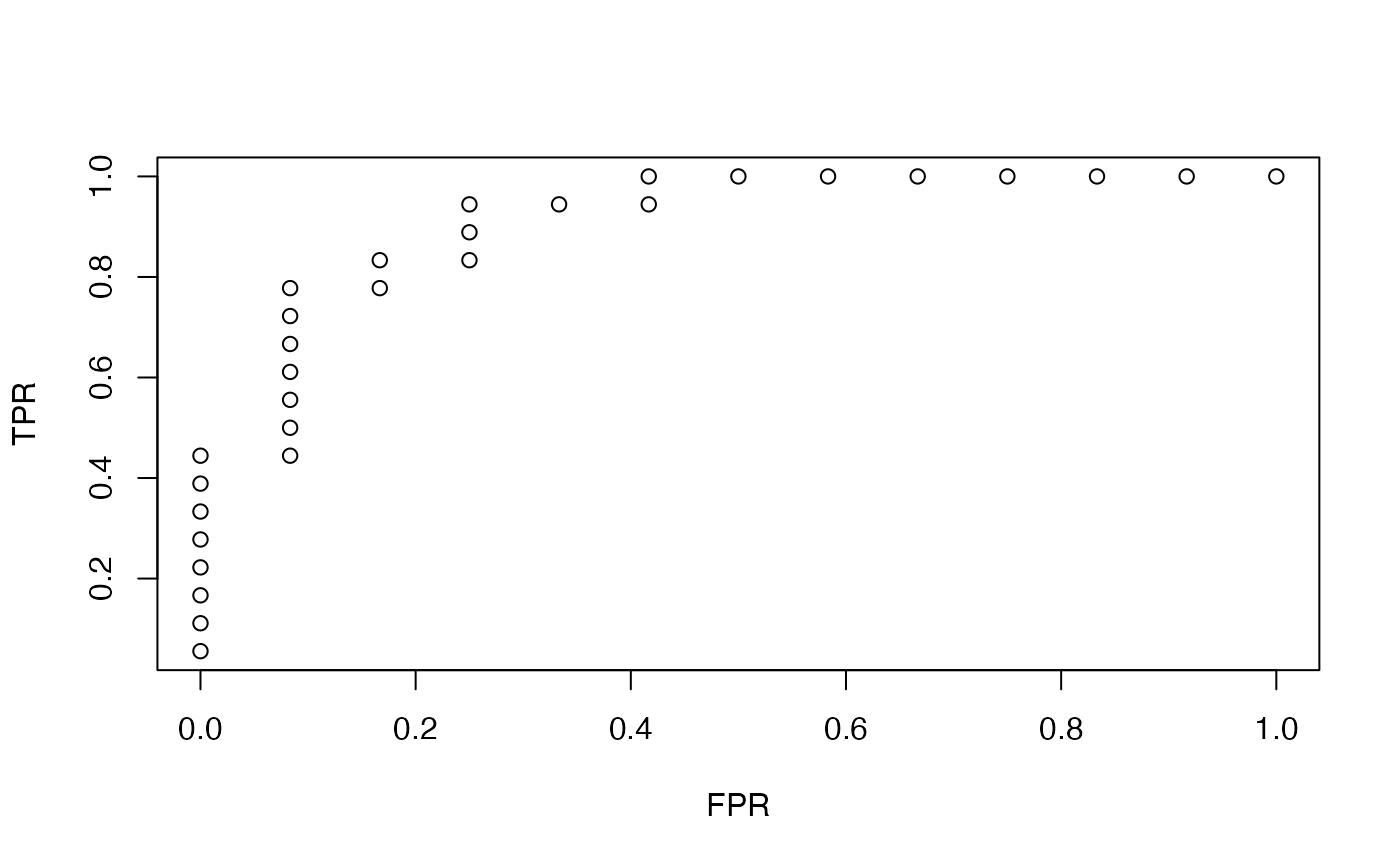 fit2c = cv.glmnet(x, y, family = "binomial", keep=TRUE)
idmin = match(fit2c$lambda.min, fit2c$lambda)
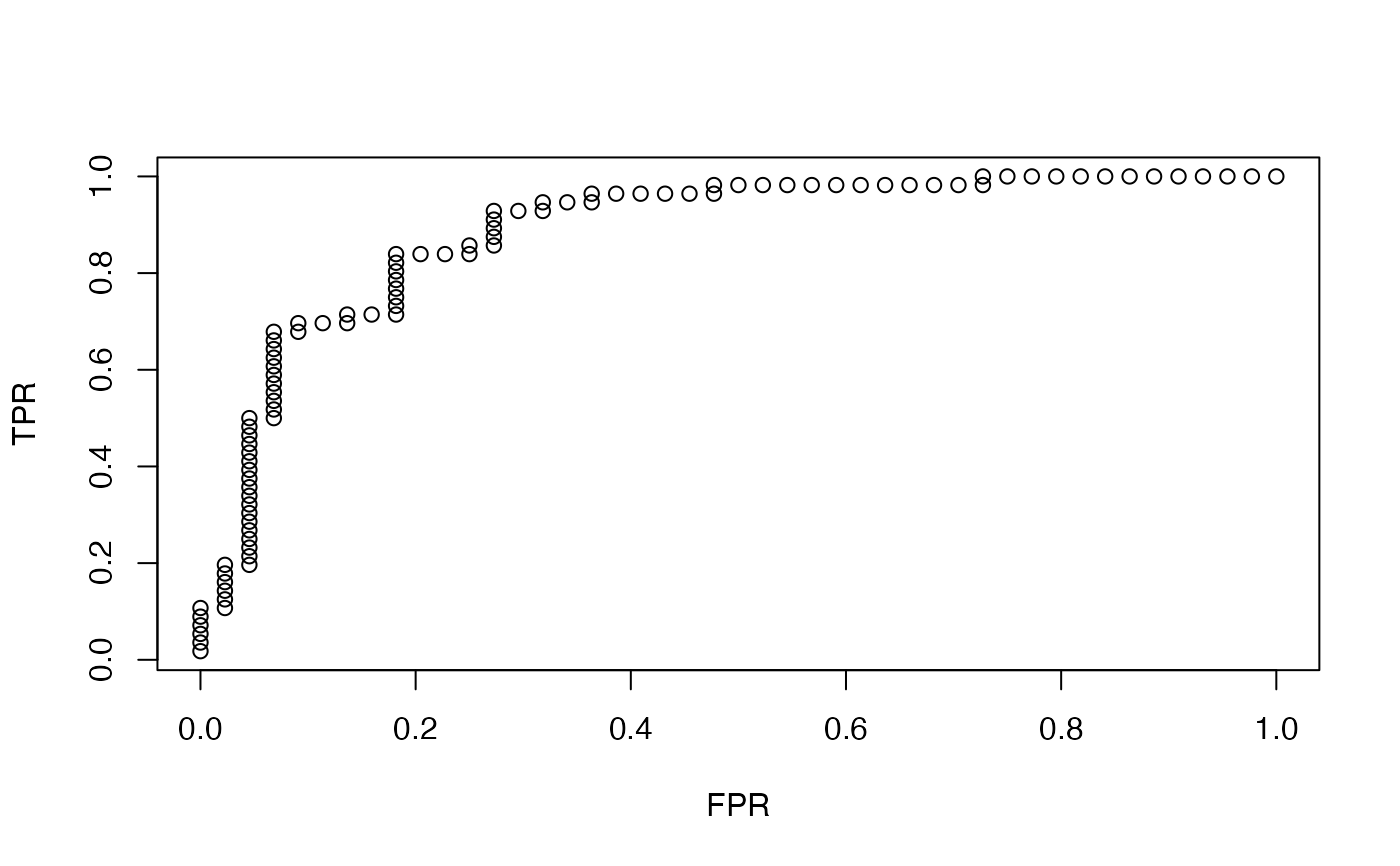
plot(roc.glmnet(fit2c$fit.preval, newy = y)[[idmin]])
fit2c = cv.glmnet(x, y, family = "binomial", keep=TRUE)
idmin = match(fit2c$lambda.min, fit2c$lambda)
plot(roc.glmnet(fit2c$fit.preval, newy = y)[[idmin]])
 data(MultinomialExample)
x <- MultinomialExample$x; y <- MultinomialExample$y
set.seed(103)
train = sample(seq(length(y)),100,replace=FALSE)
fit3 = glmnet(x[train,], y[train], family = "multinomial")
confusion.glmnet(fit3, newx = x[-train, ], newy = y[-train], s = 0.01)
#> True
#> Predicted 1 2 3 Total
#> 1 55 44 23 122
#> 2 29 82 17 128
#> 3 25 23 102 150
#> Total 109 149 142 400
#>
#> Percent Correct: 0.5975
fit3c = cv.glmnet(x, y, family = "multinomial", type.measure="class", keep=TRUE)
idmin = match(fit3c$lambda.min, fit3c$lambda)
confusion.glmnet(fit3c$fit.preval, newy = y, family="multinomial")[[idmin]]
#> True
#> Predicted 1 2 3 Total
#> 1 71 22 13 106
#> 2 39 127 26 192
#> 3 32 25 145 202
#> Total 142 174 184 500
#>
#> Percent Correct: 0.686
data(MultinomialExample)
x <- MultinomialExample$x; y <- MultinomialExample$y
set.seed(103)
train = sample(seq(length(y)),100,replace=FALSE)
fit3 = glmnet(x[train,], y[train], family = "multinomial")
confusion.glmnet(fit3, newx = x[-train, ], newy = y[-train], s = 0.01)
#> True
#> Predicted 1 2 3 Total
#> 1 55 44 23 122
#> 2 29 82 17 128
#> 3 25 23 102 150
#> Total 109 149 142 400
#>
#> Percent Correct: 0.5975
fit3c = cv.glmnet(x, y, family = "multinomial", type.measure="class", keep=TRUE)
idmin = match(fit3c$lambda.min, fit3c$lambda)
confusion.glmnet(fit3c$fit.preval, newy = y, family="multinomial")[[idmin]]
#> True
#> Predicted 1 2 3 Total
#> 1 71 22 13 106
#> 2 39 127 26 192
#> 3 32 25 145 202
#> Total 142 174 184 500
#>
#> Percent Correct: 0.686